I. Drug Stability Studies: The selection of a drug formulation is based on the comprehensive analysis of its physicochemical properties, biological characteristics, and clinical application needs. These aspects are also key issues in the research of formulations and processes. Quality studies and stability testing are essential scientific foundations for formulation screening and process optimization. Stability problems of drug preparations may arise from chemical reactions between drugs, between drugs and excipients, or with the dosage form, containers, and external substances such as air, light, moisture, etc. Impurities like metal ions, intermediates, or by-products can also cause decomposition. Factors that affect the rate of these reactions include temperature, catalysts, moisture, and light. These can be summarized as follows: (1) Temperature: For every 10°C increase, the reaction rate increases by 2–3 times. (2) Moisture: Water often acts as a necessary medium for chemical reactions. In many cases, without water, the reaction would not occur. Some chemically unstable solid drugs, such as aspirin, penicillin G potassium (sodium) salt, acetylcholine chloride, and ferrous sulfate, may adsorb moisture on their surfaces, forming a thin liquid film that leads to decomposition. (3) Acid-base catalysis: To determine if a drug is catalyzed by a buffer, it is important to keep the ionic strength constant while varying the concentration of the buffer salt (without changing the ratio to avoid pH changes). If different concentrations of buffer salts affect drug decomposition, it suggests acid-base catalysis. To minimize this effect, buffer salts should be kept at the lowest possible concentration. (4) Light: Like heat, light provides the activation energy needed for chemical reactions. Reactions such as oxidation-reduction, ring rearrangement, or hydrolysis can occur or accelerate under specific wavelengths of light, such as the hydrolysis of pentyl nitrite. Therefore, using a vapor sorption analyzer to study water adsorption behavior under different humidity conditions is crucial for drug stability research. II. Controlled Release of Multi-component Systems in Polymer: Controlled release refers to the process of binding or encapsulating a drug or substance with a polymer carrier and delivering it into a biological system. Through mechanisms like diffusion and osmosis, the active drug molecules are released at an appropriate concentration and over a sustained period, thereby maximizing the therapeutic effect. Controlled release offers advantages such as low side effects, high drug stability, and efficient utilization, making it widely studied. Water plays a significant role in the transfer of molecular substances within polymer systems. According to the theory of water adsorption in polymers, the distribution of water in the polymer is vital for controlled release and the controllable change of hydrophilic-lipophilic balance in the polymer system. III. Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients and Excipients: 1. Properties of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs): Certain physicochemical properties of APIs may affect the quality of the final formulation and the production process. These include color, odor, pH, pKa, particle size, crystal form, optical rotation, enantiomers, melting point, moisture content, solubility, oil/water partition coefficient, solvated/hydrated state, and stability under light, heat, humidity, and oxygen. For example, solubility can influence the performance of the formulation and analytical methods, making it an important factor in formulation design. Particle size may affect the dissolution of poorly soluble drugs, suspension in liquids, uniformity of content, and even bioavailability and clinical efficacy. 2. Physicochemical Properties and Dosage of Excipients: Changes in the physicochemical properties of excipients, such as molecular weight and distribution, substitution degree, viscosity, appearance, particle size and distribution, flowability, moisture content, and pH, can impact the quality of the formulation. For instance, changes in the particle size and density of diluents can affect the uniformity of content in solid dosage forms. Variations in the molecular weight or viscosity of polymeric materials used in sustained-release formulations can significantly affect the drug release profile. Moisture primarily affects solid dosage forms. For some chemically unstable drugs, the presence of a thin liquid film on the surface can lead to degradation. IV. Enzyme Preparations: Enzyme preparations include single-enzyme and multi-enzyme preparations, with the latter being more commonly used today. The relationship between moisture content and water activity in multi-enzyme additives is represented by the water adsorption isotherm. Although this relationship is not linear, the general trend is that higher moisture content corresponds to higher water activity. At higher water activity levels, the denaturation of enzyme proteins becomes more pronounced. For example, when the moisture content drops to 10%, lipase begins to lose activity only when the temperature reaches 60°C. However, when the moisture content increases to 23%, noticeable inactivation occurs at room temperature. For most enzyme preparations, keeping the water activity below 0.3 under near-neutral pH and low temperatures can prevent degradation due to protein denaturation and microbial growth, thus maintaining high enzyme activity. Traditional methods for studying moisture adsorption characteristics of materials have several limitations, including long testing times, imprecise results, and high workloads, which restrict widespread research. BESST Instruments Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd.'s 3H-2000PW Multi-Station Gravimetric Vapor Sorption Analyzer is used for fast and accurate measurement of water vapor adsorption on solid surfaces. Key features include high sensitivity, dynamic weighing range, multiple sample analysis, various gas types, large solvent storage capacity, vacuum degassing options, precise P/P0 control, and advanced automatic distillation and purification systems. The instrument also includes a nitrogen cold trap, full temperature control, and corrosion-resistant components, ensuring accuracy and safety. It supports graphical interface operation, detailed logs, voice prompts, and email notifications. With global sourcing and high-quality components, the 3H-2000PW offers excellent performance for vapor and gas adsorption studies. It comes with comprehensive reports, including adsorption isotherms, surface area analysis, pore size distribution, and thermal gravimetric analysis. The device has several patents covering its unique design, including a multi-sample setup, vapor and gas switching, and a cold trap to prevent vacuum system contamination. This makes it an ideal choice for researchers and laboratories requiring precise and reliable moisture analysis.
Relay Control Voltage Regulator
PC-TM series Relay Control Voltage Stabilizer has the low energy consumption,the over voltage protection,the low voltage protection,the over-current protection,the over-loading protection,the over-temperature protection and so on.It boasts for many kinds of protections,the collection energy conservation and the environmental protection ect.This is a brand-new concept product which possess many new technologies!This series products simultaneously ha applied for many technical monopolies
We already applied many kinds of this products patent, and the technical patent NO: 200720036394.1 and Appearance paten NO: 200730025909.3
2. Use for equipment:
Computer
Test equipment
Light system
Safe alarm system
Ray equipment
Medical equipment
Copy machine
Stereo equipment
Numerical control machine tools
Industrial automation equipment
Color and drying equipment
Test equipment
Hi-Fi equipment
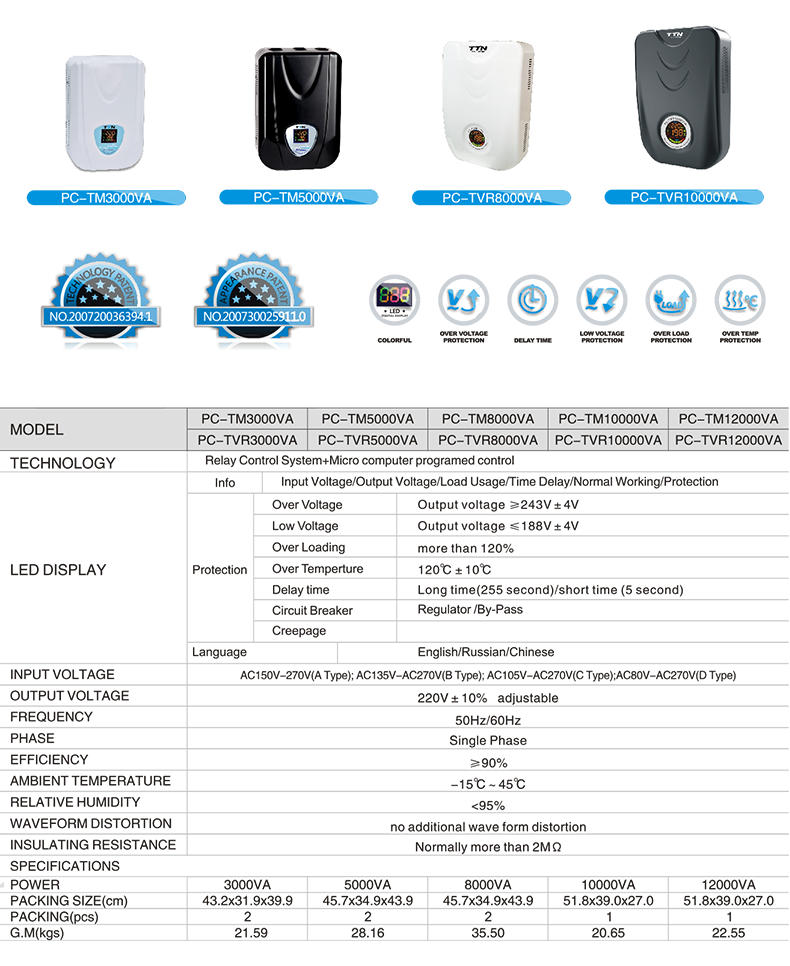



Relay Control Voltage Regulator ,Voltage Regulator For Ac,3000Va Voltage Regulator,Wall Mount Voltage Stabilzier
zhejiang ttn electric co.,ltd , https://www.ttnpower.com