New energy vehicles are sweeping the global automotive market, especially after the success of Tesla in the past two years, numerous manufacturers have begun to try to get involved in the field of new energy vehicles, with the rapid development of the market, as the main source of new energy vehicles The demand for lithium batteries is also growing rapidly, and in the foreseeable future, the growth will be considerable. Arguably, this is an outlet, but on such a well-deserved slogan, Sony has hurriedly sold its own battery business, and its battery business has become a successor to the PC business VAIO that was sold in February 2014. Abandoned. Â

Japanese electronic components company Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd. and Sony announced recently:
The two parties have reached a non-binding memorandum of understanding to confirm their intention to negotiate on the transfer of Sony’s battery business to the Murata Group. After due diligence and negotiating detailed assignment terms and conditions, Murata Manufacturing Co. and Sony Corp. are expected to sign a binding final agreement in mid-October 2016. Under the premise of obtaining the necessary regulatory approval, the two parties will The transfer was completed at the end of March 2017.
Sony's battery faces technical bottlenecks and competitionSpeaking of commercial lithium batteries, Sony is definitely the originator. According to public information, from 1975, Sony’s circle subsidiary company, Sony Energy Devices, began to operate the battery business. After more than 10 years of operation and R&D, in 1991, Sony successfully produced the world’s first rechargeable battery. Commercial lithium batteries make it possible for the popularity of mobile electronic devices.
In the lithium battery industry has a breakthrough leading position, let Sony began to pay attention to the battery business, and in the next dozen years, the company's focus on the battery business shifted from the strategic to the lithium polymer battery, in these years Among them, Sony has been trying to develop and update the battery technology to increase the energy density of the battery, but unlike Moore's Law, the energy density of a lithium battery can't be doubled like a chip in 18 months, but it needs to be Only four years can double, so Sony's growth rate in the battery industry is slow, and in recent years, the energy density of lithium batteries has approached the limit, becoming a bottleneck in the world's technology industry, the industry guessed that this is also Sony One of the incentives for the development of battery business and its sale.

Sony's early electronics products
In addition to the battery technology itself, Sony has faced fierce competition in the lithium battery industry. In the competition, Sony itself does not have an advantage. The battery it produces is not the highest in the market. Earlier, in the case of lithium batteries, Japan’s Sanyo Electronics has been dominating, and Sony and Panasonic are competing for second place. As a result, when the competition was fiercest, Matsushita made a move and acquired Sanyo Electronics directly. So far, Sony's battery business began to collapse.
In addition to the competition in the country, the rise of Korean companies such as LG and Chinese companies has caused Sony's battery business to suffer an unprecedented impact. From around 2011, Sony began planning to sell lithium battery business. Until early in 2013, the Japanese government fund tried to promote Sony's lithium battery business to a joint venture between Nissan and NEC. However, the negotiations subsequently stalled until the end of the year, "Nihon Keizai Shimbun" reported on Sunday that Sony has decided not to sell the lithium battery sector.
At the time, Sony believed that the weakening of the exchange rate of the Japanese Yen and the market’s increase in demand for smartphone batteries would help the recovery of the business. Sony said that the weak exchange rate of the Japanese yen will help Sony to increase its overseas business profits. On the other hand, the demand for some new products has also increased, so Sony will retain the lithium battery business and develop it as a core business.
Looking back now, Sony's struggle this time also did not get the growth they wanted.
Lithium battery market trialsIn addition to consumer-grade lithium batteries, Sony evaluated the automotive lithium-ion battery market twice in 2011 and 2014.
Sony said in 2011 that it will participate in the automotive lithium-ion battery business around 2015, when Sony said that after market evaluation, it is expected that the demand for lithium-ion batteries will increase substantially, so the company is negotiating with many auto manufacturers at home and abroad. At the Sony plant in the city of Ninomiya, Fukushima Prefecture, a new plant for lithium-ion battery electrodes has been built, and if demand increases, it will also consider establishing a plant overseas. However, this plan was interrupted in 2012. The reason is unknown.
In 2014, Sony once again evaluated the automotive battery market, but the target for this time was military lithium-ion vehicle batteries. At that time, Sony's growth in the field of smart phones, flat-panel and other batteries had been abnormally weak, so they chose to go with the sword. According to the announcement at the time, the military car battery had already begun research and development, and it is expected to wait until 2018 before it can be completed and put into use.
Loss and sale of battery businessThe follow-up on the R&D plans for the military vehicle battery has not shown any substantial performance from Sony. However, its battery business has been continuously losing money. In April of this year, Sony released its 2015 fiscal year results (2015.4.1-2016.3.31), which resulted in a loss of up to US$253 million in its component business. In the new fiscal year (4.1-2016.6.30 in 2016) that was just released, the loss further increased to $469 million.
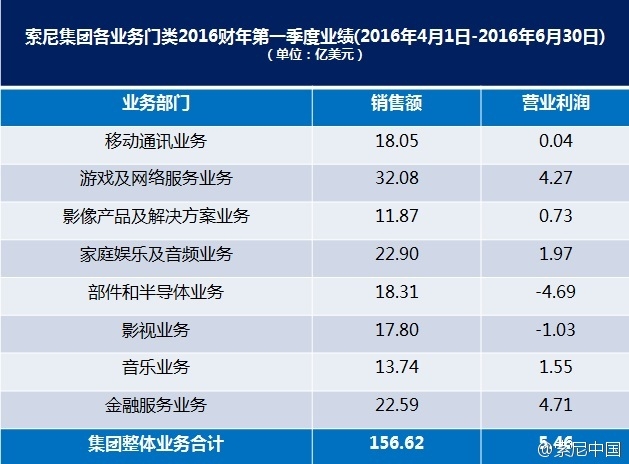
Sony's fiscal year results (2016: 2016-2016.6.30), Source: Sony China Weibo
Maybe the battery business is really "fighting Adou", so Sony intends to completely give up. As early as April and May of this year, there was news that Sony might continue to spin off non-core assets to revitalize consumer electronics products. It also said that three investment banks have contacted Sony to help them sell their battery business. Home may include Hon Hai and BYD.
In the face of this news, Sony did not respond positively. The fact that the industry was spreading in the air seemed to confirm that Sony’s default on this news was rumors that after two or three months, the incident was finally settled and Sony would Its battery business was transferred to Murata Manufacturing.
The sale of battery business is uncertainMurata Manufacturing Co., Ltd. is a well-known manufacturer of electronic components in Japan. In terms of scale, Murata is far behind Sony. The reason why it was able to purchase Sony's battery business is because Murata does have enough money and its profits are much higher than those of Sony.
Judging from the chart below: In the electrical industry, the listed company's sales rankings, Sony ranked No. 2, Murata No. 12, Sony's sales is 7 times as much as Murata. But in the profit rankings, Murata is higher than Sony, Murata 3rd, Sony 7th, Murata is 1.4 times that of Sony.

Sales ranking
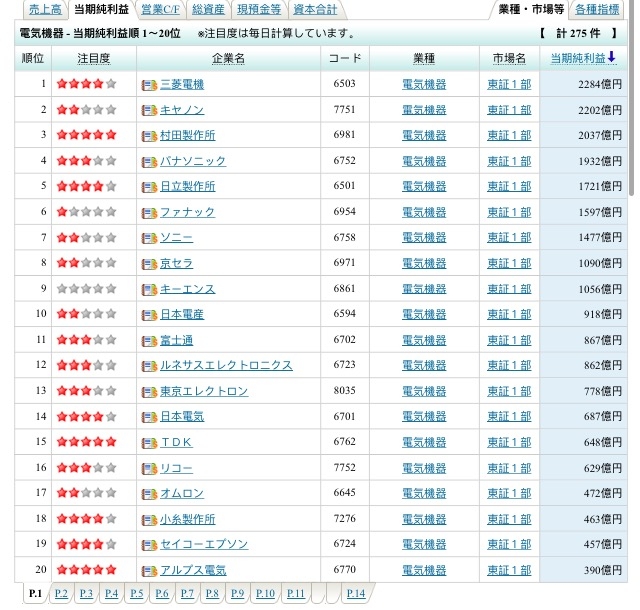
Profit rankings ( data sources )
In addition, the business of Murata's development strategy includes automotive and new energy fields, so Murata has always valued the technical strength of Sony's global battery business and Sony's experience in the international market. It is reported that after the transfer, Murata plans to operate the battery business as the core of its energy business to further realize the growth and expansion of its business and make preparations for the future to enter the automotive and new energy fields.
In terms of Sony, since Sony Group is currently looking at a stable cash flow, selling lithium battery business is not a last resort. As I said before, in the face of this "fighting A Doo", giving up is due to business risk considerations. However, as the Sony Group, which is the main revenue contributor to the consumer electronics business, losing the advantage of a free industrial chain is not a good choice. In the future, it will be even more difficult for a Korean company with a complete vertical industrial chain to compete.
From Sony's first launch of commercial lithium batteries to the sale of lithium battery business today, in the past 20 years or so, the former industry pioneers have lagged behind rising stars, and people have to feel the changes in the technology industry. Abandoning the impact of lithium battery business on Sony, it is still not good to make a final conclusion, it is good or bad time to test.

bluetooth earpods
bluetooth earpods
Guangzhou Ysure Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.ysurecase.com